Modex EnSAVes
- contact:
-
project group :Energy Markets and Energy Systems Analysis
Transport and Energy - funding:
Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy
- partner:
Technische Universität Dresden, Lehrstuhl für Energiewirtschaft;
Fraunhofer-Institut für System- und Innovationsforschung;
Universität Duisburg-Essen, Lehrstuhl für Energiewirtschaft;
ESA² GmbH, Energy Systems Analysis Associates;
M-FIVE GmbH Mobility, Futures, Innovation, Economics - start:
01/2019
- end:
12/2021
Background
In the course of the energy turnaround, a completely new energy landscape is developing in Germany with increasing networking and the resulting interactions between the large number of players and new technologies. Model-based energy system analyses are an important tool for understanding these complex interrelationships and mechanisms. On this basis, targeted impulses can be given to drive system development in the desired direction. To this end, a wide variety of model approaches have been developed over the past decades, which now cover a very broad methodological spectrum. In order to guarantee the transparency of the system analysis and at the same time to stimulate the continuous improvement of the models, comparative comparisons of the approaches should be carried out at regular intervals in the framework of model experiments. The project outlined in the following is intended to carry out a methodologically oriented model comparison based on a concrete application case.
Aim, topic and methodology of the model comparison
The aim of the model comparison is to compare the results of different model approaches for the market ramp-up of new electricity applications. The model experiment focuses on the areas of electromobility and heat pumps in the residential building sector, for which the consortium uses various detailed models with a specific analysis focus. Since investment decisions for passenger cars and building heating systems are made by different actors, there are many different influencing factors that are represented differently in the individual model approaches. At the same time, the dynamics of development in this area are decisive for the path towards an "all-electric society", as is often called for with regard to the implementation of ambitious climate protection targets.
At the same time, increased electrification is also expected to have an impact on supply security, and the question arises in particular of how critical supply situations such as a cold "dark lull" in winter can be managed in future. Therefore, demand development models are to be coupled with electricity market models. The latter are to be used specifically for an analysis of future generation security in the sense of "generation adequacy", i.e. the adequacy of generation and other back-up capacities to cope with periods of high residual load. To this end, future expected load curves for the new electricity applications are derived from the demand-side models and used as input for the electricity market models.
These are then used to investigate whether and how electricity demand can be met in the future during the course of the year by exploiting the flexibility potential of the generation plants and demand applications. In particular, the focus will be on a year with extreme weather conditions. In this case, the 2012 weather year with extremely low temperatures at the beginning of February would be a good place to look. By comparing the results of different electricity market models, it will be possible to determine how the modelling of flexibility potentials affects generation security.
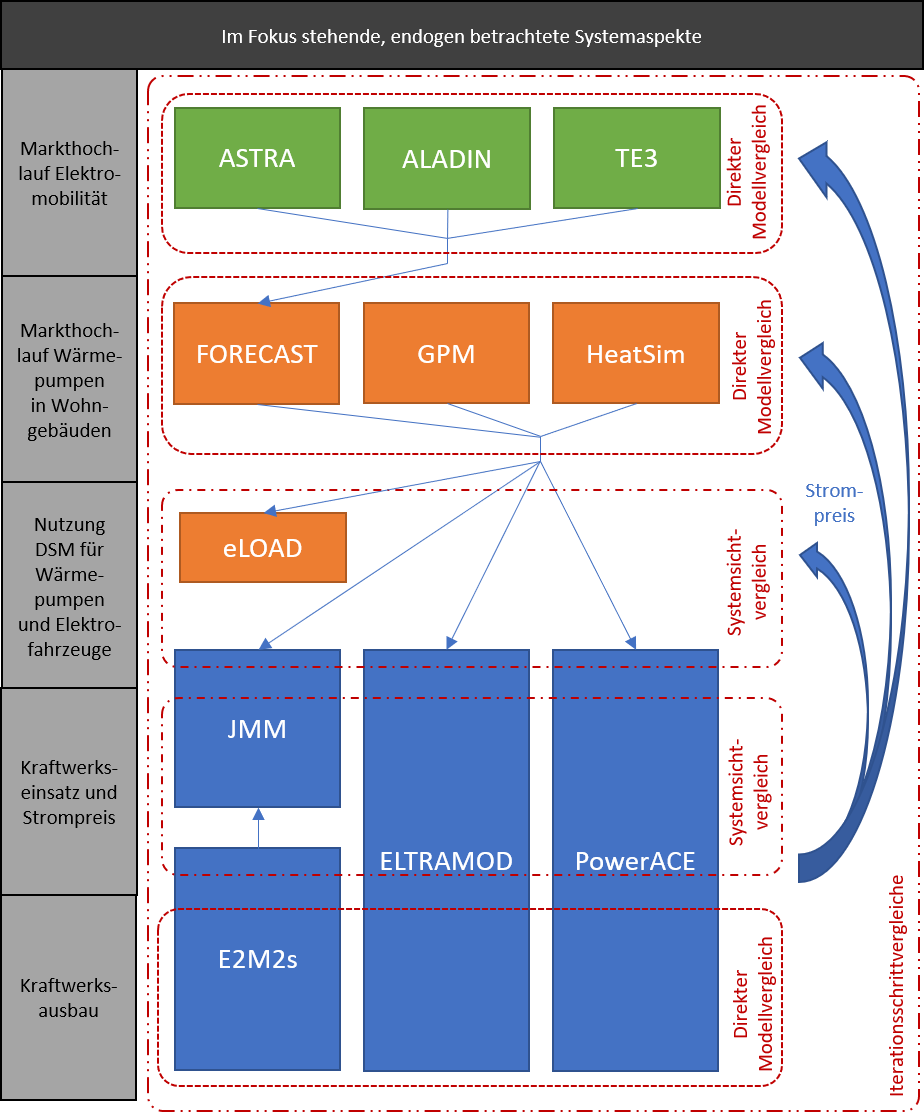
Figure 1: Overview of the design of the model comparison
